NextGen Ag Service
Pathogen Facts
- Tar spot, caused by the fungal pathogen Phyllachora maydis, is a relatively new foliar disease of corn in the United States, first appearing in Illinois and Indiana in 2015.
- Look for tar spot to develop during cool temperatures (60-70 ºF, 16-20 ºC), high relative humidity (>75%), frequent cloudy days, and 7+ hours of dew at night.
- Tar spot reduces yield by reducing the photosynthetic capacity of leaves and causing rapid premature leaf senescence.
Identification and Symptoms of Tar Spot
- Tar spot is the physical manifestation of circular-sharped, tar colored fungal fruiting bodies, called ascomata, developing on corn leaves.
- Initial symptoms are small brown lesions that darken with age.
- The texture of the leaf becomes bumpy and uneven when the fruiting bodies are present.
- Tar spot lesions cannot be rubbed away completely or dissolved in water.
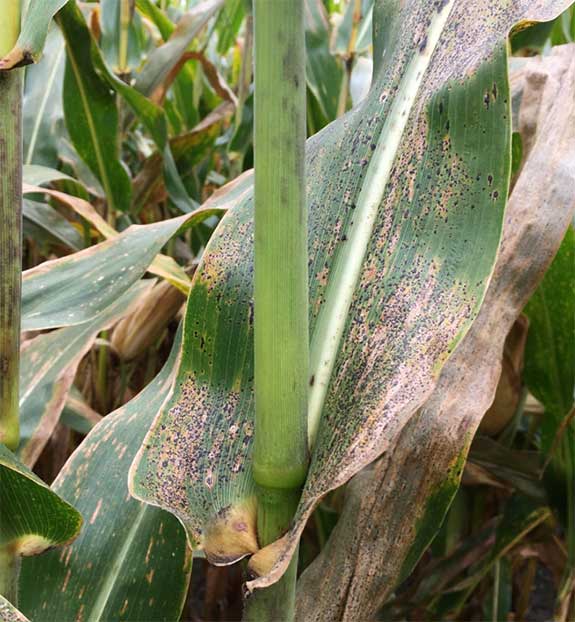

Corn leaves infected with tar spot in a field in Illinois in 2018.
- Under favorable conditions, tar spot spreads from the lowest leaves to the upper leaves, leaf sheathes, and eventually the husks of the developing ears.
- Severe infection can cause leaf necrosis.
- Affected ears can have reduced weight and loose kernels, and kernels at the ear tip may germinate prematurely.

Corn leaf under magnification showing dense coverage with tar spot ascomata.
Tar Spot Occurrence in the U.S.
- Tar spot in corn was first observed over a century ago in high valleys in Mexico.
- The first confirmations of tar spot in the U.S. were in Illinois and Indiana in 2015 (Bissonnette, 2015; Ruhl et al., 2016).
- It has subsequently spread to Michigan, Wisconsin, Iowa, Ohio, Missouri, Minnesota, Pennsylvania, and southern Ontario (Figure 1).
- Tar spot has also been found in four counties in southern Florida.
- In 2018, tar spot established itself as an economic concern for corn production in the Midwest, with severe outbreaks reported in several states.
“Genetic resistance to tar spot should be the number one consideration when seeking to manage this disease, as it appears to have a greater impact on symptoms and yield loss than either cultural or chemical management practices."
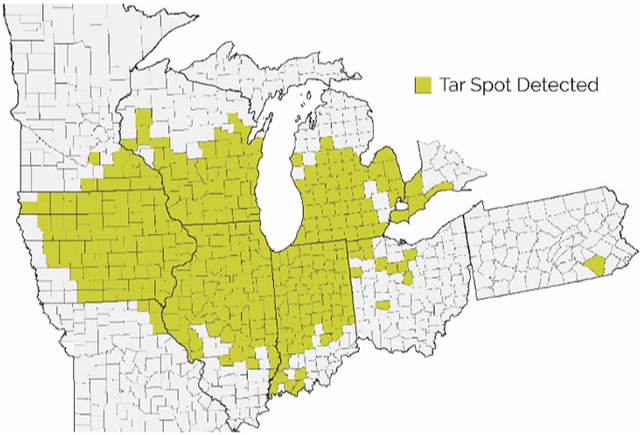
Figure 1. Counties with confirmed incidence of tar spot, 2015-2020 (as of 10-12-20). Source: Corn ipmPIPE, 2020.
Tar Spot Epidemiology
- P. maydis is an obligate pathogen, which means it needs a living host to grow and reproduce. It is capable of overwintering in the Midwestern U.S. in infected crop residue on the soil surface.
- Tar spot is more likely to develop during cool temperatures (60-70 ºF, 16-20 ºC), high relative humidity (>75%), frequent cloudy days, and 7+ hours of dew at night.
- Tar spot is polycyclic and can continue to produce spores and spread to new plants as long as environmental conditions are favorable.
- P. maydis produces windborne spores that have been shown to disperse up to 800 ft. Spores are released during periods of high humidity.
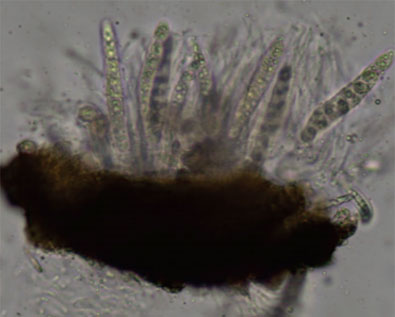
Microscopic view of fungal spores of P. maydis.
Management Considerations
Yield Impact of Tar Spot
- 2018 was the first time that corn yield reductions associated with tar spot were documented in the U.S.
- University corn hybrid trials conducted in 2018 suggested potential yield losses of up to 39 bu/acre under heavy infestations (Telenko et al., 2019).
- Severe tar spot infestations have been associated with reduced stalk quality. If foliar symptoms are present, monitor stalk quality carefully to determine harvest timing.
- There is no evidence that tar spot causes ear rot or produces harmful mycotoxins (Kleczewski, 2018).
Differences in Hybrid Response
- Observations in hybrid trials indicate that hybrids differ in susceptibility to tar spot (Kleczewski and Smith, 2018).
- Longer maturity hybrids for a given location have been shown to have a greater risk of yield loss from tar spot than shorter maturity hybrids (Telenko et al., 2019).
- Genetic resistance to tar spot should be the number one consideration when seeking to manage this disease, as it appears to have a greater impact on symptoms and yield loss than either cultural or chemical management practices.
Foliar Fungicides
- Several foliar fungicides are labeled for control of tar spot in corn (Table 1).
- Field research on tar spot has been limited so far, but has shown that fungicides can reduce tar spot symptoms and help protect yield.
- Specific management recommendations for fungicides in the Midwestern U.S. are still being developed.
Table 1. Efficacy of fungicides labeled for tar spot in corn (Wise, 2020).
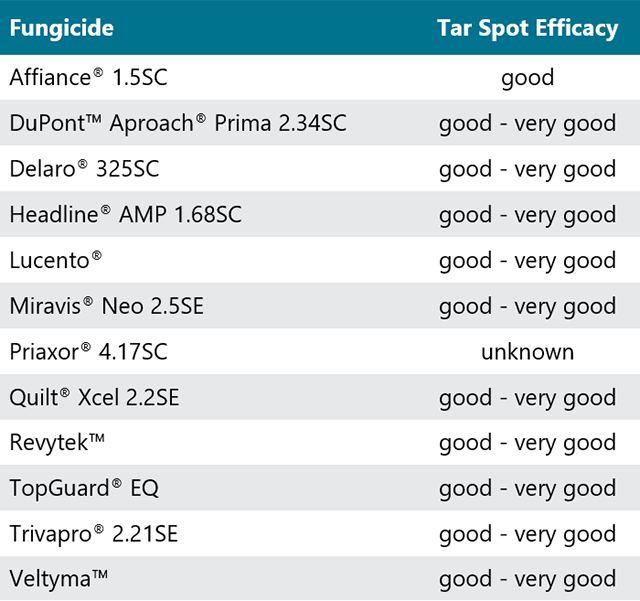
Fungicide application timing is extremely important and needs to be made near the onset of the tar spot symptoms. Efficacy ratings based on limited site locations from 2018 and 2019. A 2(ee) label is available for several fungicides for control of tar spot, however, efficacy data are limited. Check 2(ee) labels carefully, as not all products have 2(ee) labels in all states.
- Research suggests that tar spot may be challenging to control with a single fungicide application due to its rapid reinfection cycle, particularly in irrigated corn.
Agronomic Practices to Manage Tar Spot
- The pathogen that causes tar spot overwinters in corn residue. How the amount of residue on a field’s soil surface affects disease severity the following year is unknown.
- Observations so far suggest that rotation and tillage probably have little effect on tar spot severity.
- Duration of leaf surface wetness appears to be a key factor in the development and spread of tar spot. Farmers with irrigated corn in areas affected by tar spot have experimented with irrigating at night to reduce the duration of leaf wetness.
Corn and Soybean Scouting Calendar
Download your copy of Pioneer's Corn and Soybean Scouting Calendar. It's your guide to the diseases and pests that threaten your yield and when to look for each one.
References
- Bissonnette, S. 2015. CORN DISEASE ALERT: New Fungal Leaf disease “Tar spot” Phyllachora maydis identified in 3 northern Illinois counties. The Bulletin. University of Illinois Extension.
- Kleczewski, N. 2018. Tar Spot on Corn: Setting the Record Straight. Illinois Field Crop Disease Hub. University of Illinois Extension.
- Kleczewski, N. and D. Smith. 2018. Corn Hybrid Response to Tar Spot. The Bulletin. University of Illinois Extension.
- Ruhl G., M.K. Romberg, S. Bissonnette, D. Plewa, T. Creswell, and K.A. Wise 2016. First report of tar spot on corn caused by Phyllachora maydis in the United States. Plant Dis 100(7):1496.
- Telenko, D., M.I. Chilvers, N. Kleczewski, D.L. Smith, A.M. Byrne, P. Devillez, T. Diallo, R. Higgins, D. Joos, K. Kohn, J. Lauer, B. Mueller, M.P. Singh, W.D. Widdicombe, and L.A. Williams. 2019. How tar spot of corn impacted hybrid yields during the 2018 Midwest epidemic. Crop Protection Network.
- Wise, K. 2020. Fungicide Efficacy for Control of Corn Diseases. Crop Protection Network. CPN-2011-W.
Aproach® Prima is not registered for sale or use in all states. Contact your state pesticide regulatory agency to determine if a product is registered for sale or use in your state. Always read and follow label directions.
The foregoing is provided for informational use only. Please contact your Pioneer sales professional for information and suggestions specific to your operation. Product performance is variable and depends on many factors such as moisture and heat stress, soil type, management practices and environmental stress as well as disease and pest pressures. Individual results may vary.